Iterative Graph Processing
Gelly利用了Flink的高效迭代操作以支持大型迭代图计算。目前我们提供了Vertex Centric,Scatter Gather和Gather Sum Apply模型的实现。接下来的章节中,我们描述了这些抽象并展示了如何在Gelly中使用它们。
- Vertex Centric迭代计算
- Vertex Centric迭代计算配置
- Scatter Gather迭代计算
- Scatter Gather迭代计算配置
- Gather Sum Apply迭代计算
- Gather Sum Apply迭代计算配置
- 迭代计算抽象对比
Vertex Centric迭代计算
Vertex Centric模型,也称为”像顶点一样思考”或”Pregel”,通过图顶点的角度表达计算。 该计算在迭代的每一步(称为超步)中同步地处理,在每个超步时,每个顶点执行一个UDF(User Defined Function)。 顶点之间通过消息进行通讯,任何一个顶点可以给图中任何其他的顶点发送消息,只要知道它的ID即可。
下面的图中展示该计算模型,虚线框和并行单元对应。在每个超步中,所有的活跃顶点并行执行相同的用户定义的计算。因为超步时同步执行的,因此每次超步中发送的消息都被保证发送了到下次超步的开始。
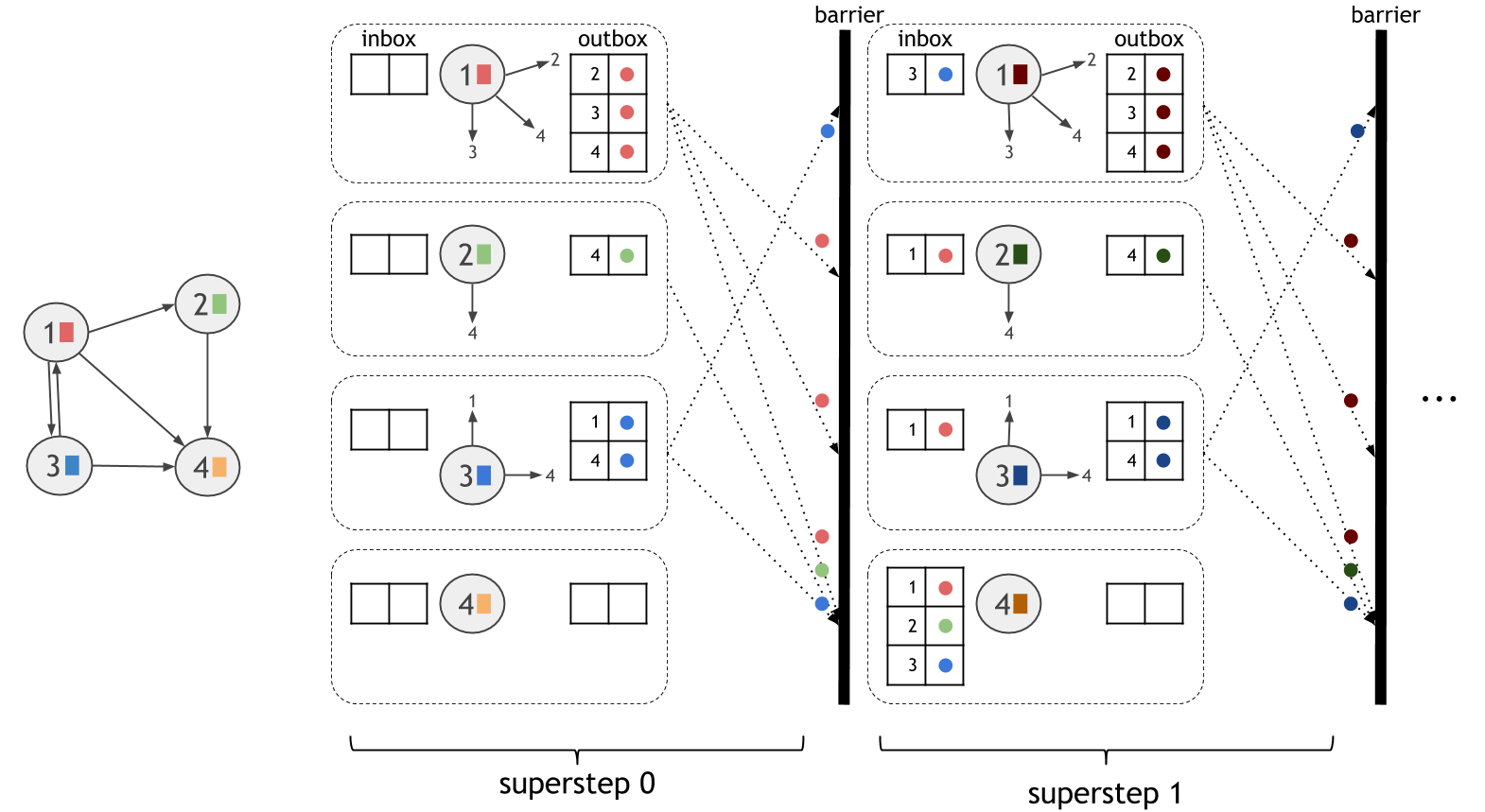
在Gelly中使用Vertex Centric迭代,用户只需要定义顶点的计算函数ComputeFunction即可。
该函数和最大迭代次数通过Gelly的runVertexCentricIteration函数参数指定。该方法在输入图上执行Vertex Centric迭代计算,并输出更新后顶点值的新图。可选的MessageCombiner函数可以被用于减少通信消耗。
让我们考虑基于Vertex Centric的单源点最短路径算法(SSSP)。算法开始时,除了源顶点初始值为0,每个顶点初始值为正无穷。第一次超步计算时,源顶点将距离传播给它的邻居。在接下来的超步中,每个顶点检查接收的消息并选择其中最小的距离值。如果该距离值比顶点当前值小,则更新顶点的值,并产生消息发送给其邻居。如果顶点在超步中没有更新它的值,则在下次超步时不会发送任何消息给它的邻居。当没有顶点的值发生更新或者达到了最大的超步迭代次数,算法将会收敛。在这个算法中,Message Combiner可以被用来减少发送给目标顶点的消息个数。
// read the input graph
Graph<Long, Double, Double> graph = ...
// define the maximum number of iterations
int maxIterations = 10;
// Execute the vertex-centric iteration
Graph<Long, Double, Double> result = graph.runVertexCentricIteration(
new SSSPComputeFunction(), new SSSPCombiner(), maxIterations);
// Extract the vertices as the result
DataSet<Vertex<Long, Double>> singleSourceShortestPaths = result.getVertices();
// - - - UDFs - - - //
public static final class SSSPComputeFunction extends ComputeFunction<Long, Double, Double, Double> {
public void compute(Vertex<Long, Double> vertex, MessageIterator<Double> messages) {
double minDistance = (vertex.getId().equals(srcId)) ? 0d : Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
for (Double msg : messages) {
minDistance = Math.min(minDistance, msg);
}
if (minDistance < vertex.getValue()) {
setNewVertexValue(minDistance);
for (Edge<Long, Double> e: getEdges()) {
sendMessageTo(e.getTarget(), minDistance + e.getValue());
}
}
}
// message combiner
public static final class SSSPCombiner extends MessageCombiner<Long, Double> {
public void combineMessages(MessageIterator<Double> messages) {
double minMessage = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
for (Double msg: messages) {
minMessage = Math.min(minMessage, msg);
}
sendCombinedMessage(minMessage);
}
}// read the input graph
val graph: Graph[Long, Double, Double] = ...
// define the maximum number of iterations
val maxIterations = 10
// Execute the vertex-centric iteration
val result = graph.runVertexCentricIteration(new SSSPComputeFunction, new SSSPCombiner, maxIterations)
// Extract the vertices as the result
val singleSourceShortestPaths = result.getVertices
// - - - UDFs - - - //
final class SSSPComputeFunction extends ComputeFunction[Long, Double, Double, Double] {
override def compute(vertex: Vertex[Long, Double], messages: MessageIterator[Double]) = {
var minDistance = if (vertex.getId.equals(srcId)) 0 else Double.MaxValue
while (messages.hasNext) {
val msg = messages.next
if (msg < minDistance) {
minDistance = msg
}
}
if (vertex.getValue > minDistance) {
setNewVertexValue(minDistance)
for (edge: Edge[Long, Double] <- getEdges) {
sendMessageTo(edge.getTarget, vertex.getValue + edge.getValue)
}
}
}
// message combiner
final class SSSPCombiner extends MessageCombiner[Long, Double] {
override def combineMessages(messages: MessageIterator[Double]) {
var minDistance = Double.MaxValue
while (messages.hasNext) {
val msg = inMessages.next
if (msg < minDistance) {
minDistance = msg
}
}
sendCombinedMessage(minMessage)
}
}Vertex Centric迭代计算配置
Vertex Centric迭代计算可以使用VertexCentricConfiguration对象进行配置。
目前有如下参数可以指定:
-
名称: Vertex Centric迭代计算的名称,该名称在日志和消息中显示,并可以使用
setName()进行指定。 -
并行度: 迭代计算的并行度,可以使用
setParallelism()进行指定。 -
堆内Solution Set: 定义了Solution Set是否保存在堆内内存(Flink内部对象的序列化方式)中,还是保存在简单的对象表中。默认情况下,Solution Set保存在堆内内存中,该属性可以通过
setSolutionSetUnmanagedMemory()方法进行设置。 -
聚合器: 迭代聚合器可以使用
registerAggregator()方法进行注册,迭代聚合器可以将每次超步的聚合结果合并起来,并使得在下次超步中可以访问它们。注册后的聚合器可以在用户定义的ComputeFunction的内部进行访问。 -
广播变量: 可以使用
addBroadcastSet()方法将数据集作为广播变量添加到ComputeFunction。
Graph<Long, Double, Double> graph = ...
// configure the iteration
VertexCentricConfiguration parameters = new VertexCentricConfiguration();
// set the iteration name
parameters.setName("Gelly Iteration");
// set the parallelism
parameters.setParallelism(16);
// register an aggregator
parameters.registerAggregator("sumAggregator", new LongSumAggregator());
// run the vertex-centric iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
Graph<Long, Long, Double> result =
graph.runVertexCentricIteration(
new Compute(), null, maxIterations, parameters);
// user-defined function
public static final class Compute extends ComputeFunction {
LongSumAggregator aggregator = new LongSumAggregator();
public void preSuperstep() {
// retrieve the Aggregator
aggregator = getIterationAggregator("sumAggregator");
}
public void compute(Vertex<Long, Long> vertex, MessageIterator inMessages) {
//do some computation
Long partialValue = ...
// aggregate the partial value
aggregator.aggregate(partialValue);
// update the vertex value
setNewVertexValue(...);
}
}val graph: Graph[Long, Long, Double] = ...
val parameters = new VertexCentricConfiguration
// set the iteration name
parameters.setName("Gelly Iteration")
// set the parallelism
parameters.setParallelism(16)
// register an aggregator
parameters.registerAggregator("sumAggregator", new LongSumAggregator)
// run the vertex-centric iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
val result = graph.runVertexCentricIteration(new Compute, new Combiner, maxIterations, parameters)
// user-defined function
final class Compute extends ComputeFunction {
var aggregator = new LongSumAggregator
override def preSuperstep {
// retrieve the Aggregator
aggregator = getIterationAggregator("sumAggregator")
}
override def compute(vertex: Vertex[Long, Long], inMessages: MessageIterator[Long]) {
//do some computation
val partialValue = ...
// aggregate the partial value
aggregator.aggregate(partialValue)
// update the vertex value
setNewVertexValue(...)
}
}Scatter Gather迭代计算
Scatter Gather模型,也称为”signal/collect”模型,通过图顶点的角度表达计算。该计算在迭代的每一步(称为超步)中同步地处理,在每个超步时,每个顶点为其他顶点产生消息,并基于它接受到的消息更新自己的值。在Gelly使用Scatter Gather迭代计算,用户只需要定义每次超步中每个顶点的行为即可:
- Scatter: 产生一个顶点发送给其他顶点的消息。
- Gather: 使用接收到的消息更新顶点的值。
Gelly为Scatter Gather迭代计算提供了方法,用户只需要实现两个函数,与scatter和gather阶段相对应。第一个函数是ScatterFunction,它允许顶点向其他顶点发送消息,消息将会在它们被发送所在的超步时被接收。第二个函数是GatherFunction,它定义了顶点如何基于接收到的消息更新自己的值。
这些函数和最大迭代次数通过Gelly的runScatterGatherIteration函数参数指定。该方法在输入图上执行Vertex Centric迭代计算,并输出更新后顶点值的新图。
一次Scatter Gather迭代可以使用类如总顶点数、入度和出度等信息进行扩展。
另外,Scatter Gather迭代运行使用的邻居类型(in/out/all)也可以被指定。默认情况下,来自输入邻居的更新将会修改当前顶点的状态,而消息将发送给输出的邻居。
让我们考虑使用Scatter Gather迭代模型计算单源点最短路径的算法(SSSP),下面的图中顶点1是原点。每次超步中,每个顶点发送候选的距离消息到它的邻居,消息的值是当前顶点值与连接到该顶点的边的权值之和。当收到候选的距离消息时,每个顶点计算最小的距离,如果更短的路径被计算出来,顶点的值就会被更新。如果顶点在超步中没有更改它的值,那么它就不会产生下次超步中发送给邻居的消息。该算法在没有顶点值更新时收敛。
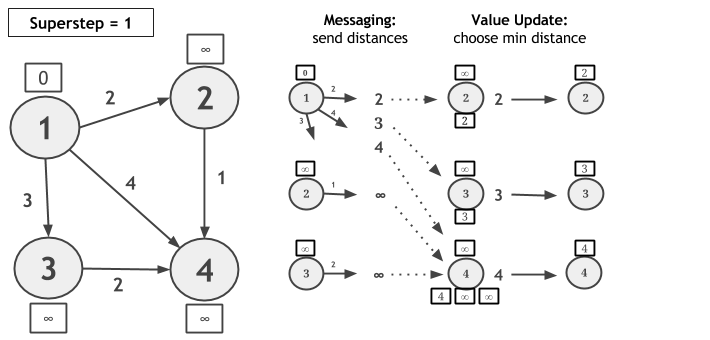
// read the input graph
Graph<Long, Double, Double> graph = ...
// define the maximum number of iterations
int maxIterations = 10;
// Execute the scatter-gather iteration
Graph<Long, Double, Double> result = graph.runScatterGatherIteration(
new MinDistanceMessenger(), new VertexDistanceUpdater(), maxIterations);
// Extract the vertices as the result
DataSet<Vertex<Long, Double>> singleSourceShortestPaths = result.getVertices();
// - - - UDFs - - - //
// scatter: messaging
public static final class MinDistanceMessenger extends ScatterFunction<Long, Double, Double, Double> {
public void sendMessages(Vertex<Long, Double> vertex) {
for (Edge<Long, Double> edge : getEdges()) {
sendMessageTo(edge.getTarget(), vertex.getValue() + edge.getValue());
}
}
}
// gather: vertex update
public static final class VertexDistanceUpdater extends GatherFunction<Long, Double, Double> {
public void updateVertex(Vertex<Long, Double> vertex, MessageIterator<Double> inMessages) {
Double minDistance = Double.MAX_VALUE;
for (double msg : inMessages) {
if (msg < minDistance) {
minDistance = msg;
}
}
if (vertex.getValue() > minDistance) {
setNewVertexValue(minDistance);
}
}
}// read the input graph
val graph: Graph[Long, Double, Double] = ...
// define the maximum number of iterations
val maxIterations = 10
// Execute the scatter-gather iteration
val result = graph.runScatterGatherIteration(new MinDistanceMessenger, new VertexDistanceUpdater, maxIterations)
// Extract the vertices as the result
val singleSourceShortestPaths = result.getVertices
// - - - UDFs - - - //
// messaging
final class MinDistanceMessenger extends ScatterFunction[Long, Double, Double, Double] {
override def sendMessages(vertex: Vertex[Long, Double]) = {
for (edge: Edge[Long, Double] <- getEdges) {
sendMessageTo(edge.getTarget, vertex.getValue + edge.getValue)
}
}
}
// vertex update
final class VertexDistanceUpdater extends GatherFunction[Long, Double, Double] {
override def updateVertex(vertex: Vertex[Long, Double], inMessages: MessageIterator[Double]) = {
var minDistance = Double.MaxValue
while (inMessages.hasNext) {
val msg = inMessages.next
if (msg < minDistance) {
minDistance = msg
}
}
if (vertex.getValue > minDistance) {
setNewVertexValue(minDistance)
}
}
}Scatter Gather迭代计算配置
Scatter Gather迭代可以使用ScatterGatherConfiguration对象进行配置。
目前有以下参数可以被指定:
-
名称: Scatter Gather迭代计算的名称,该名称在日志和消息中显示,并可以使用
setName()进行指定。 -
并行度: 迭代计算的并行度,可以使用
setParallelism()进行指定。 -
堆内Solution Set: 定义了Solution Set是否保存在堆内内存(Flink内部对象的序列化方式)中,还是保存在简单的对象表中。默认情况下,Solution Set保存在堆内内存中,该属性可以通过
setSolutionSetUnmanagedMemory()方法进行设置。 -
聚合器: 迭代聚合器可以使用
registerAggregator()方法进行注册,迭代聚合器可以将每次超步的聚合结果合并起来,并使得在下次超步中可以访问它们。注册后的聚合器可以在用户定义的ScatterFunction和GatherFunction的内部进行访问。 -
广播变量: 可以分别使用
addBroadcastSetForUpdateFunction()和addBroadcastSetForMessagingFunction()方法将数据集作为广播变量添加到ScatterFunction和GatherFunction。 -
顶点数: 允许迭代内部访问顶点总数,该属性可以通过
setOptNumVertices()方法设置。
在顶点更新函数和消息传播函数内可以使用getNumberOfVertices()函数访问顶点数。如果该选型未设置,方法返回-1。
- 度: 允许迭代内部访问顶点的出度或入度,该属性可以通过
setOptDegrees()方法设置。
在scatter和gather函数内可以使用getInDegree()和getInDegree()函数访问顶点的入度和出度。如果度选项未设置,方法返回-1。
- 消息传播方向: 默认情况下,顶点发送消息给它的邻居,并基于从邻居接收到的消息更新自身的值。该配置选项允许用户更改消息传播的方向,取值EdgeDirection.IN
,EdgeDirection.OUT和EdgeDirection.ALL。相应地,消息传播方向决定了更新接受消息的方向为EdgeDirection.OUT,EdgeDirection.IN和EdgeDirection.ALL。该属性可以通过setDirection()`方法进行设置。
Graph<Long, Double, Double> graph = ...
// configure the iteration
ScatterGatherConfiguration parameters = new ScatterGatherConfiguration();
// set the iteration name
parameters.setName("Gelly Iteration");
// set the parallelism
parameters.setParallelism(16);
// register an aggregator
parameters.registerAggregator("sumAggregator", new LongSumAggregator());
// run the scatter-gather iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
Graph<Long, Double, Double> result =
graph.runScatterGatherIteration(
new Messenger(), new VertexUpdater(), maxIterations, parameters);
// user-defined functions
public static final class Messenger extends ScatterFunction {...}
public static final class VertexUpdater extends GatherFunction {
LongSumAggregator aggregator = new LongSumAggregator();
public void preSuperstep() {
// retrieve the Aggregator
aggregator = getIterationAggregator("sumAggregator");
}
public void updateVertex(Vertex<Long, Long> vertex, MessageIterator inMessages) {
//do some computation
Long partialValue = ...
// aggregate the partial value
aggregator.aggregate(partialValue);
// update the vertex value
setNewVertexValue(...);
}
}val graph: Graph[Long, Double, Double] = ...
val parameters = new ScatterGatherConfiguration
// set the iteration name
parameters.setName("Gelly Iteration")
// set the parallelism
parameters.setParallelism(16)
// register an aggregator
parameters.registerAggregator("sumAggregator", new LongSumAggregator)
// run the scatter-gather iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
val result = graph.runScatterGatherIteration(new Messenger, new VertexUpdater, maxIterations, parameters)
// user-defined functions
final class Messenger extends ScatterFunction {...}
final class VertexUpdater extends GatherFunction {
var aggregator = new LongSumAggregator
override def preSuperstep {
// retrieve the Aggregator
aggregator = getIterationAggregator("sumAggregator")
}
override def updateVertex(vertex: Vertex[Long, Long], inMessages: MessageIterator[Long]) {
//do some computation
val partialValue = ...
// aggregate the partial value
aggregator.aggregate(partialValue)
// update the vertex value
setNewVertexValue(...)
}
}下面的例子展示了度数和顶点数选项的使用。
Graph<Long, Double, Double> graph = ...
// configure the iteration
ScatterGatherConfiguration parameters = new ScatterGatherConfiguration();
// set the number of vertices option to true
parameters.setOptNumVertices(true);
// set the degree option to true
parameters.setOptDegrees(true);
// run the scatter-gather iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
Graph<Long, Double, Double> result =
graph.runScatterGatherIteration(
new Messenger(), new VertexUpdater(), maxIterations, parameters);
// user-defined functions
public static final class Messenger extends ScatterFunction {
...
// retrieve the vertex out-degree
outDegree = getOutDegree();
...
}
public static final class VertexUpdater extends GatherFunction {
...
// get the number of vertices
long numVertices = getNumberOfVertices();
...
}val graph: Graph[Long, Double, Double] = ...
// configure the iteration
val parameters = new ScatterGatherConfiguration
// set the number of vertices option to true
parameters.setOptNumVertices(true)
// set the degree option to true
parameters.setOptDegrees(true)
// run the scatter-gather iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
val result = graph.runScatterGatherIteration(new Messenger, new VertexUpdater, maxIterations, parameters)
// user-defined functions
final class Messenger extends ScatterFunction {
...
// retrieve the vertex out-degree
val outDegree = getOutDegree
...
}
final class VertexUpdater extends GatherFunction {
...
// get the number of vertices
val numVertices = getNumberOfVertices
...
}下面的例子展示了边方向选项的使用,顶点更新的值包含它的输入邻居列表。
Graph<Long, HashSet<Long>, Double> graph = ...
// configure the iteration
ScatterGatherConfiguration parameters = new ScatterGatherConfiguration();
// set the messaging direction
parameters.setDirection(EdgeDirection.IN);
// run the scatter-gather iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
DataSet<Vertex<Long, HashSet<Long>>> result =
graph.runScatterGatherIteration(
new Messenger(), new VertexUpdater(), maxIterations, parameters)
.getVertices();
// user-defined functions
public static final class Messenger extends GatherFunction {...}
public static final class VertexUpdater extends ScatterFunction {...}val graph: Graph[Long, HashSet[Long], Double] = ...
// configure the iteration
val parameters = new ScatterGatherConfiguration
// set the messaging direction
parameters.setDirection(EdgeDirection.IN)
// run the scatter-gather iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
val result = graph.runScatterGatherIteration(new Messenger, new VertexUpdater, maxIterations, parameters)
.getVertices
// user-defined functions
final class Messenger extends ScatterFunction {...}
final class VertexUpdater extends GatherFunction {...}Gather Sum Apply迭代计算
就像Scatter Gather模型,Gather Sum Apply也在迭代步骤中同步执行,即超步。每个超步包含以下部分:
- Gather: 一个在边和对应顶点邻居上并行调用的UDF,产生一个局部值。
- Sum: 用户定义的聚合函数,讲Gather产生的局部值合并为一个单一值。
- Apply: 通过该函数将Sum产生的聚合值更新到每个顶点的当前值。
让我们考虑使用GSA迭代模型计算单源点最短路径的算法(SSSP),下面的图中顶点1是原点。在Gather阶段,我们通过累加每个顶点的值和边的权值计算新的候选距离。在Sum阶段,候选距离通过顶点ID分组,并选择最小的距离。在Apply阶段,新计算出来的距离将会和当前顶点的值,二者之间的最小值将会被设为顶点的新值。
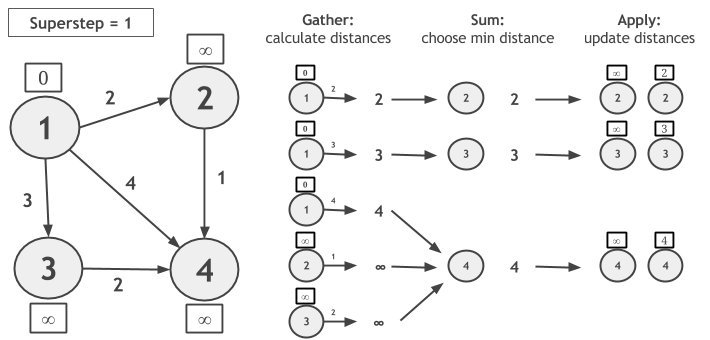
需要注意的是,如果顶点在超步中没有更新它的值,将不会在下次超步中计算候选距离。当没有顶点值发生更新时,算法收敛。
使用Gelly GSA实现该例子,用户只需要在输入图上调用runGatherSumApplyIteration方法,并提供GatherFunction,SumFunction和ApplyFunction用户定义函数。迭代的同步、分组、值更新和收敛由框架处理。
// read the input graph
Graph<Long, Double, Double> graph = ...
// define the maximum number of iterations
int maxIterations = 10;
// Execute the GSA iteration
Graph<Long, Double, Double> result = graph.runGatherSumApplyIteration(
new CalculateDistances(), new ChooseMinDistance(), new UpdateDistance(), maxIterations);
// Extract the vertices as the result
DataSet<Vertex<Long, Double>> singleSourceShortestPaths = result.getVertices();
// - - - UDFs - - - //
// Gather
private static final class CalculateDistances extends GatherFunction<Double, Double, Double> {
public Double gather(Neighbor<Double, Double> neighbor) {
return neighbor.getNeighborValue() + neighbor.getEdgeValue();
}
}
// Sum
private static final class ChooseMinDistance extends SumFunction<Double, Double, Double> {
public Double sum(Double newValue, Double currentValue) {
return Math.min(newValue, currentValue);
}
}
// Apply
private static final class UpdateDistance extends ApplyFunction<Long, Double, Double> {
public void apply(Double newDistance, Double oldDistance) {
if (newDistance < oldDistance) {
setResult(newDistance);
}
}
}// read the input graph
val graph: Graph[Long, Double, Double] = ...
// define the maximum number of iterations
val maxIterations = 10
// Execute the GSA iteration
val result = graph.runGatherSumApplyIteration(new CalculateDistances, new ChooseMinDistance, new UpdateDistance, maxIterations)
// Extract the vertices as the result
val singleSourceShortestPaths = result.getVertices
// - - - UDFs - - - //
// Gather
final class CalculateDistances extends GatherFunction[Double, Double, Double] {
override def gather(neighbor: Neighbor[Double, Double]): Double = {
neighbor.getNeighborValue + neighbor.getEdgeValue
}
}
// Sum
final class ChooseMinDistance extends SumFunction[Double, Double, Double] {
override def sum(newValue: Double, currentValue: Double): Double = {
Math.min(newValue, currentValue)
}
}
// Apply
final class UpdateDistance extends ApplyFunction[Long, Double, Double] {
override def apply(newDistance: Double, oldDistance: Double) = {
if (newDistance < oldDistance) {
setResult(newDistance)
}
}
}注意gather将Neighbor类型作为参数,这个方便的类型简单包装了顶点和它的邻边。
想要了解更多如何使用Gather Sum Apply模型实现算法,请查看GSAPageRank and GSAConnectedComponents提供的Gelly库方法。
Gather Sum Apply迭代计算配置
GSA迭代计算可以通过GSAConfiguration对象进行配置。
目前以下参数可以被指定:
-
名称: GSA迭代计算的名称,该名称在日志和消息中显示,并可以使用
setName()进行指定。 -
并行度: 迭代计算的并行度,可以使用
setParallelism()进行指定。 -
堆内Solution Set: 定义了Solution Set是否保存在堆内内存(Flink内部对象的序列化方式)中,还是保存在简单的对象表中。默认情况下,Solution Set保存在堆内内存中,该属性可以通过
setSolutionSetUnmanagedMemory()方法进行设置。 -
聚合器: 迭代聚合器可以使用
registerAggregator()方法进行注册,迭代聚合器可以将每次超步的聚合结果合并起来,并使得在下次超步中可以访问它们。注册后的聚合器可以在用户定义的GatherFunction,SumFunction和ApplyFunction的内部进行访问。 -
广播变量: 可以分别使用
addBroadcastSetForGatherFunction(),addBroadcastSetForSumFunction()和addBroadcastSetForApplyFunction方法将数据集作为广播变量添加到GatherFunction,SumFunction和ApplyFunction。 -
顶点数: 允许迭代内部访问顶点总数,该属性可以通过
setOptNumVertices()方法设置。
在gather,sum和apply函数内可以使用getNumberOfVertices()函数访问顶点数。如果该选型未设置,方法返回-1。
- 边方向: 默认情况下会收集顶点输出邻居的值,该方向可以使用
setDirection()修改。
下面的例子展示了顶点数选项的使用。
Graph<Long, Double, Double> graph = ...
// configure the iteration
GSAConfiguration parameters = new GSAConfiguration();
// set the number of vertices option to true
parameters.setOptNumVertices(true);
// run the gather-sum-apply iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
Graph<Long, Long, Long> result = graph.runGatherSumApplyIteration(
new Gather(), new Sum(), new Apply(),
maxIterations, parameters);
// user-defined functions
public static final class Gather {
...
// get the number of vertices
long numVertices = getNumberOfVertices();
...
}
public static final class Sum {
...
// get the number of vertices
long numVertices = getNumberOfVertices();
...
}
public static final class Apply {
...
// get the number of vertices
long numVertices = getNumberOfVertices();
...
}val graph: Graph[Long, Double, Double] = ...
// configure the iteration
val parameters = new GSAConfiguration
// set the number of vertices option to true
parameters.setOptNumVertices(true)
// run the gather-sum-apply iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
val result = graph.runGatherSumApplyIteration(new Gather, new Sum, new Apply, maxIterations, parameters)
// user-defined functions
final class Gather {
...
// get the number of vertices
val numVertices = getNumberOfVertices
...
}
final class Sum {
...
// get the number of vertices
val numVertices = getNumberOfVertices
...
}
final class Apply {
...
// get the number of vertices
val numVertices = getNumberOfVertices
...
}下面的例子展示了边方向选项的使用。
Graph<Long, HashSet<Long>, Double> graph = ...
// configure the iteration
GSAConfiguration parameters = new GSAConfiguration();
// set the messaging direction
parameters.setDirection(EdgeDirection.IN);
// run the gather-sum-apply iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
DataSet<Vertex<Long, HashSet<Long>>> result =
graph.runGatherSumApplyIteration(
new Gather(), new Sum(), new Apply(), maxIterations, parameters)
.getVertices();val graph: Graph[Long, HashSet[Long], Double] = ...
// configure the iteration
val parameters = new GSAConfiguration
// set the messaging direction
parameters.setDirection(EdgeDirection.IN)
// run the gather-sum-apply iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
val result = graph.runGatherSumApplyIteration(new Gather, new Sum, new Apply, maxIterations, parameters)
.getVertices()迭代计算抽象对比
虽然Gelly提供的三种迭代计算抽象看起来很相似,然而理解它们之间的差别可以为程序提供更高的性能和可维护性。
以上三者之中,Vertex Centric模型是最通用的模型,并支持任意的计算和消息发送。Scatter Gather模型中,生产消息的逻辑和更顶点新的逻辑解耦。因此使用Scatter Gather模型开发的程序更容易跟进和维护。
将消息发送阶段和顶点更新逻辑分开,不仅让程序更容易跟进,更能对性能产生积极的影响。因为不需要同时访问存储接收消息和发送消息的数据结构,传统方式实现的Scatter Gather模型有更低的内存需求。然而,这个特性也限制了算法的表达能力,使得一些计算模式变得不够直观。自然地,如果一个算法需要顶点同时访问接收消息和发送消息的存储,那么使用Scatter Gather进行表示将会出现问题。强连通分量和近似最大权匹配算法就是类似的算法。这个限制的直接后果,就是顶点在同一个阶段中,无法既生成消息又更新状态。从而,要决定是否传播消息,就需要存储点的值,以便下一次迭代的gather阶段可以访问得到。如果顶点更新逻辑包含对邻边权值的计算,这就需要内部包含一个从scatter到gather阶段的特殊消息。因此,通常的解决办法将会导致更高的内存消耗,降低代码的优雅性,从而导致算法实现更难被理解。
GSA迭代模型和Scatter Gather模型也很相似。实际上,任何使用GSA表达的算法都可以使用Scatter Gather模型实现。Scatter Gather模型的消息发送阶段和GSA的Gather和Sum阶段等价:Gather可以被看作消息的生产阶段,Sum可以被看作消息路由到目标顶点的阶段。而顶点更新阶段和Apply步骤相对应。
二者实现的最主要的差别是GSA的Gather阶段是基于边的并行计算,而Scatter Gather的消息发送阶段是基于顶点的并行计算。结合上边SSSP的例子,我们可以看到在Scatter Gather例子的第一个超不中,顶点1、2、3并行产生消息,顶点1生产了3条消息,而顶点2和3各生产了一条消息。而在GSA的例子中,计算是基于边并行的:顶点1的三个候选的距离值是并行产生的。因此,如果Gather阶段包含了大量计算,使用GSA进行传播计算将是更好的方案,而不是加重一个顶点的计算。另外一种情况就是当输入图是倾斜(一些顶点相对于其他顶点拥有更多的邻居)的时候,基于边的并行计算会更加高效。
两者的另外一个区别就是Scatter Gather模型内部使用了coGroup,而GSA使用reduce进行计算。因此,如果计算中合并消息的函数需要全组的值,就应该使用Scatter Gather模型。如果更新函数是可结合、可交换的,那么GSA的聚合操作将是更高效的实现,因为它可以利用组合的特性。
另外需要注意的是,GSA需要严格地在邻居上执行,而Vertex Centric和Scatter Gather模型,顶点可以给任何已知ID的顶点发送消息,而不管这个顶点是否是自己的邻居。最后,在Gelly的Scatter Gather实现中,用户可以选择消息传播的方向,而GSA尚不能支持该特性,因此每个顶点只能基于它的输入邻居的值进行更新。
Gelly的迭代计算模型之间的主要差别如下表所示。
| Iteration Model | Update Function | Update Logic | Communication Scope | Communication Logic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertex-Centric | arbitrary | arbitrary | any vertex | arbitrary |
| Scatter-Gather | arbitrary | based on received messages | any vertex | based on vertex state |
| Gather-Sum-Apply | associative and commutative | based on neighbors' values | neighborhood | based on vertex state |
